CE-TEK Co., Ltd.
R&D
CUSTOMER CENTER

- Technology Introduction
HOME > R&D > Technology Introduction
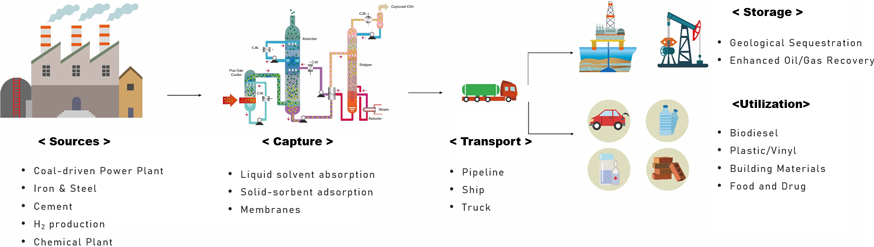
CCUS technical definition
CCUS(Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage)
Carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS), also referred to as carbon capture, utilization, and sequestration, is a process that captures carbon dioxide emissions from sources like coal-fired power plants and either reuses or stores them so that they do not enter the atmosphere.
< Concept map of CCUS >
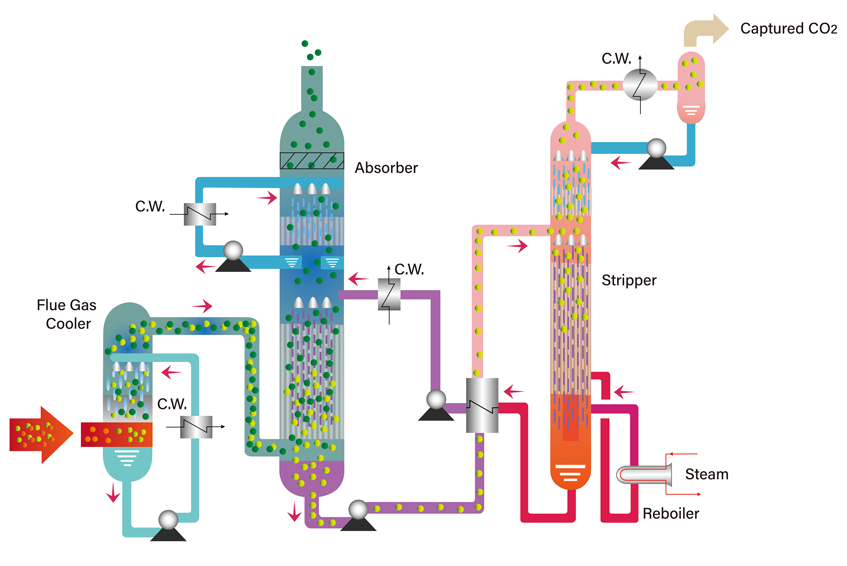
Amine-based post-combustion CO2 capture
< Schematic of amine-based post-combustion CO2 capture process >
(Principle) : The combustion flue gas enters an absorber and flows in a direction counter to the current of the CO2-lean solvent, in which CO2 is absorbed, and the CO2-rich solvent is pumped to a stripper for regeneration. In the stripper, the CO2-rich solvent is heated to break down the CO2 and regenerate the original solvent for reuse.
(Representative amine solvent) : MEA (Monoethanolamine), DEA (Diethanolamine), MDEA (N-methyldiethanolamine)
(Process configuration) : The process components consists of pre-scrubber, absorber, stripper, reboiler, and R/L cross heat exchanger. The pre-scrubber removes SO2 together with dust in the flue gas. In the absorber, the solvent reacts with CO2 from the flue gas; then, in the stripper, the weak intermediate compound formed between solvent and CO2 is broken down by applying thermal energy supplied from the reboiler. The R/L cross heat exchanger enables the process to efficiently recover thermal energy from the hot lean loading solvent and move it to the cold rich loading solvent.